Homocitrullin ist eine organisch-chemische Verbindung, speziell ein L-Lysin-Derivat mit einer Carbamoyl-Gruppe an Position N6; auf Grund des asymmetrischen C-Atoms sind zwei stereoisomere Formen möglich, von denen biochemisch jedoch nur das L-Homocitrullin von Bedeutung ist:
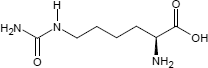 | 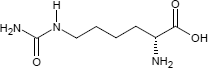 |
| L-Homocitrullin N6-Carbamoyl-L-lysin (CAS 1190-49-4) | D-Homocitrullin N6-Carbamoyl-D-lysin (CAS 121080-96-4) |
Namentlich leitet sich die Substanzbezeichnug vom [[Citrullin]] ab; homo weist darauf hin, dass sich im Vergleich zum Citrullin eine zusätzliche Methylen-Gruppe in der Kohlenstoffkette des Homocitrullins befindet.
Homocitrullin zählt zu den Aminosäuren; sie findet sich als Stoffwechselprodukt des Lysins beim Menschen und anderen Säugetieren und tritt bei gewissen Krankheitsformen an Proteinen bzw. Peptiden gebunden auf [1, 2].
Datenblatt: Homocitrullin
Quellen und weitere Informationen:
[1] - Sanna Turunen, Marja-Kaisa Koivula, Jukka Melkko, Eeva Alasaarela, Petri Lehenkari, Juha Risteli:
Different amounts of protein-bound citrulline and homocitrulline in foot joint tissues of a patient with anti-citrullinated protein antibody positive erosive rheumatoid arthritis.
In: Journal of Translational Medicine, (2013), DOI 10.1186/1479-5876-11-224.
[2] - Sanna Turunen, Pekka Hannonen, Marja-Kaisa Koivula, Leila Risteli, Juha Risteli:
Separate and overlapping specificities in rheumatoid arthritis antibodies binding to citrulline- and homocitrulline-containing peptides related to type I and II collagen telopeptides.
In: Arthritis Research and Therapy, (2015), DOI 10.1186/s13075-014-0515-z.
[3] - Aurore Desmons, Stephane Jaisson, Christine Pietrement, Philippe Rieu, Alain Wynckel, Philippe Gillery:
Homocitrulline: a new marker for differentiating acute from chronic renal failure.
In: Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, (2015), DOI 10.1515/cclm-2015-0398.
Aktualisiert am 21.11.2018.
Permalink: https://www.internetchemie.info/chemie-lexikon/stoffe/h/homocitrullin.php
© 1996 - 2026 Internetchemie ChemLin