Zu den Acetoniden (Isopropylidenacetale) zählen cyclische Acetale aus Aceton und Diolen oder Polyhydroxy-Verbindungen, wie zum Beispiel das Glycerolacetonid (Solketal; (2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methanol):
Die Funktionalisierung von 1,2- und 1,3-Diolen zu Isopropylidenacetal-Gruppen ist eine häufig verwendete Schutzgruppen-Methode in der organischen Synthese. Die Entfernung der Acetonid-Schutzgruppe erfolgt leicht durch Hydrolyse des Acetals mit wäßriger Säure unter Rückbildung der 1,2- bzw. 1,3-Diole.
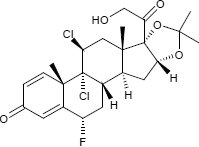
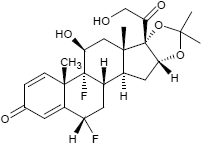
Pharmazeutische Wirkstoffe mit einer Acetonid-Gruppe sind die nachfolgend aufgeführten Corticosteroide, die in der Dermatologie eingesetzt werden; die Acetonid-Gruppe erleichtert hierbei die Aufnahme der Wirkstoffe durch die Haut:
 |
 |
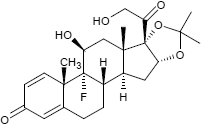 |
| Fluclorolonacetonid | Fluocinolonacetonid | Triamcinolonacetonid |
| C24H29Cl2FO5 | C24H30F2O6 | C24H31FO6 |
| CAS 3693-39-8 | CAS 67-73-2 | CAS 76-25-5 |
| ATC-Code: D07AC02 | ATC-Code: D07AC04 u.a. | ATC-Code: kein |
Quellen und weitere Informationen:
[1] - Acetonides.
Definition im IUPAC Gold Book, DOI 10.1351/goldbook.A00064.
[2] - Acetonides.
Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, Organic Chemistry Portal.
Kategorie: Stoffgruppen
Aktualisiert am 22. Juni 2023.
Permalink: https://www.internetchemie.info/chemie-lexikon/stoffgruppen/a/acetonide.php
© 1996 - 2026 Internetchemie ChemLin