Die Aurone bilden eine Gruppe organisch-chemischer, flavonoider Verbindungen, zu denen neben den Stammverbindungen die davon abgeleiteten (stabileren und in der Natur häufiger auftretenden) (Z)-Derivate sowie die (selteneren) (E)-Derivate zählen:
| E-Auron | |||
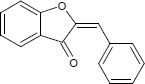 | |||
| IUPAC: | (2E)-2-Benzyliden-1-benzofuran-3(2H)-on | ||
| Bezeichnungen: | 2-Benzyliden-coumaran-3-on | ||
| Summenformel: | C15H10O2 | Molare Masse = | 222,24 g mol-1 |
| InChI Std.: | OMUOMODZGKSORV-GXDHUFHOSA-N | CAS RN = | 75318-34-2 |
| Datenquellen: | ChemSpider, PubChem | ||
| Z-Auron | |||
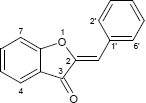 | |||
| IUPAC: | (2Z)-2-Benzyliden-1-benzofuran-3(2H)-on | ||
| Summenformel: | C15H10O2 | Molare Masse = | 222,24 g mol-1 |
| InChI Std.: | OMUOMODZGKSORV-UVTDQMKNSA-N | CAS RN = | 37542-14-6 |
| Datenquellen: | ChemSpider, PubChem, ChEMBL | ||
Namensgeber dieser O-heterocyclischen Stoffgruppe ist die goldgelbe Farbe der Blütenblätter des Mädchenauges (Coreopsis grandiflora), dessen Farbpigmente ein Auron enthalten [1, 2]. Darüber hinaus wurden Aurone im Löwenmäulchen (Antirrhinum), in Kosmeen (Cosmos, Schmuckkörbchen), in Braunalgen (Spatoglossum variabile), in Gomphrena agrestis (E-Derivat) und anderen aufgefunden.
Quellen und weitere Informationen
[1] - T. A. Geissman, William Mojé:
The Pigments of Coreopsis grandiflora.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, (1951), DOI 10.1021/ja01156a080.
[2] - E. C. Bate-Smith, T. A. Geissmann:
Benzalcoumaranones.
Nature, (1951), DOI 10.1038/167688a0.
[3] - Loránd Farkas, László Pallos:
Aurone und Auron-glykoside. Synthese und endgültiger Strukturbeweis des Bracteins, eines Glucosids aus Helichrysum bracteatum (Vent.) Willd.
Chemische Berichte, (1965), DOI 10.1002/cber.19650980922.
[4] - Toru Nakayama et al.:
Specificity analysis and mechanism of aurone synthesis catalyzed by aureusidin synthase, a polyphenol oxidase homolog responsible for flower coloration.
FEBS Letters, (2001), DOI 10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02529-7.
[5] - Toru Nakayama:
Enzymology of aurone biosynthesis.
Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, (2002), DOI 10.1016/S1389-1723(02)80184-0.
[6] - Nicholas J. Lawrence et al.:
The total synthesis of an aurone isolated from Uvaria hamiltonii.
Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, (2003), DOI 10.1016/j.bmcl.2003.07.003.
[7] - Martin Wichers:
Darstellung tetracyclischer Diltiazem-Analoga aus Auronen und Thioauronen.
Dissertation Pharmazeutische Chemie, TU Braunschweig, (2004), urn:nbn:de:gbv:084-6047.
[8] - Kevin M. Davis et al.:
Characterisation of aurone biosynthesis in Antirrhinum majus.
Physiologia Plantarum, (2006), DOI 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00774.x.
[9] - Eiichiro Ono et al.:
Yellow flowers generated by expression of the aurone biosynthetic pathway.
PNAS, (2006), DOI 10.1073/pnas.0604246103.
[10] - Tran Thu Huong et al.:
A new prenylated aurone from Artocarpus altilis.
Journal of Asian Natural Products Research, (2012), DOI 10.1080/10286020.2012.702758.
[11] - Carole Dubois et al.:
Versatile Effects of Aurone Structure on Mushroom Tyrosinase Activity.
ChemBioChem, (2012), DOI 10.1002/cbic.201100716.
Kategorie: Stoffgruppen
Aktualisiert am 23. Juni 2023.
Permalink: https://www.internetchemie.info/chemie-lexikon/stoffgruppen/a/aurone.php
© 1996 - 2026 Internetchemie ChemLin