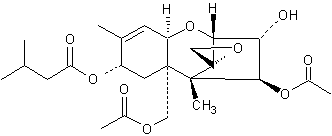
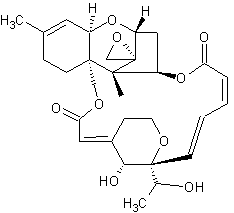
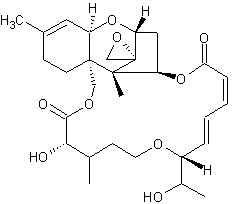
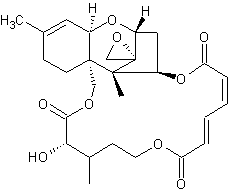
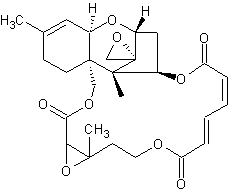
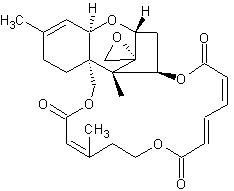
Die Trichothecene bilden eine Gruppe verschiedener sequiterpenoider Naturstoffe, die als sekundäre Stoffwechselprodukte von Schimmelpilzen u. a. den Mykotoxinen zugeordnet werden.
Chemisch charakteristisch für das tetracyclische 12-Epoxytrichothec-9-en-Ringsystem der Trichothecene ist neben der Sesquiterpen-Struktur insbesondere eine Epoxid-Funktion, die auch für die Giftigkeit dieser Stoffgruppe verantwortlich ist:
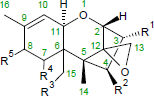
Unterschieden werden vier Trichithecen-Gruppen, die sich in einigen chemischen Funktionen unterscheiden: Trichothecen Typ A, B, C und D:
Typ A:
Keine Keto-Gruppe (Carbonyl-Funktion) an Kohlenstoffatom C-8. Stärker toxisch, als B-Typ.
Beispiele: Diacetoxyscirpenol, HT-2 Toxin, Monoacetoxyscirpenol, Neosolaniol, T-2 Toxin, Trichodermin.
Typ B:
Keto-Gruppe (Carbonylfunktion) an C-8. Weniger toxisch, als A-Typ
Beispiele: 3-Acetyldeoxynivalenol, 15-Acetyldeoxynivalenol, Deoxynivalenol, Fusarenon X, Nivalenol.
Typ C:
Zweite Epoxid-Gruppe an C7/C8 oder C9/10
Beispiele: Crotocin, Baccharin.
Typ D:
Makrocyclische Derivate mit Ringstrukturen zwischen C4 und C15 sowie Esterbindungen.
Zum Beispiel: Myrotoxin B, Roridin A, Satratoxin H, Verrucarin A
Namensgeber der Naturstoffgruppe ist der Schimmelpilz Trichothecium roseum, aus dem 1948 erstmals Trichothecene isoliert und charakterisiert wurden [1]. Insgesamt sind die Verbindungen dieser Stoffklasse - wie deren Produzenten - weit verbreitet und kommen unter anderem in folgenden Pilzen vor:
Cephalosporium sp.
Fusarium sp. (Fusarien-Toxine, z. B.: F. equiseti, F. graminearum, F. langsethiae, F. poae, F. sporotrichioides)
Myrothecium sp.
Podostroma cornu-damae
Trichoderma sp.
Trichothecium sp.
Verticimonosporium sp.
Stachybotrys sp.
Stachybotrys chartarum
Beispiele für Trichothecene
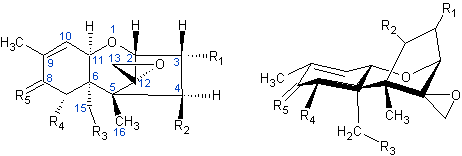 |
| Allgemeine Struktur der Trichothecene |
Tabelle: Trichothecene |
R1 |
R2 |
R3 |
R4 |
R5 |
| OH |
H |
OH |
OH |
O |
|
|
Dehydronivalenolacetat |
Ac |
H |
OH |
OH |
O |
|
Diacetoxyscirpenol |
OH |
OAc |
OAc |
H |
H |
|
Diacetylnivalenol |
OH |
OAc |
OAC |
OH |
O |
| OH |
OAc |
OH |
OH |
O |
|
|
HT2-Toxin |
OH |
OH |
OAc |
H |
(CH3)2CHCH2OCO |
|
Neosolaniol |
OH |
OAc |
OAc |
H |
OH |
| OH |
OH |
OH |
OH |
O |
|
|
T2-Toxin |
OH |
OAc |
OAc |
H |
(CH3)2CHCH2OCO |
|
Tetraacetylnivalenol |
OAc |
OAc |
OAc |
OAc |
O |
|
Trichothecin |
H |
CH3CH=CHOCO |
H |
H |
O |
| H |
OH |
H |
H |
O |
T2-Toxin
|
Strukturformel:
|
C24H34O9 - CAS Nr. 21259-20-1 Löslich in Dichlormethan, DMSO, Ethanol, Ethylacetat. Leicht löslich in Petrolether; Wasser. Kristallisiert als farbloses Pulver aus Dichlormethan; Schmelzpunkt: 151 - 152 °C. |
Makrocyclische Trichothecene
|
|
Satratoxin H C29H36O9 - CAS 53126-64-0 Vorkommen: Myrothecium verrucaria; Stachybotrys chartarum PubChem [10328045, Roridin A Daten] |
|
|
Roridin A C29H40O9 - CAS 14729-29-4 Vorkommen: Myrothecium verrucaria; M. roridum Literatur: Enzyme immunoassay for the macrocyclic trichothecene roridin A: production, properties, and use of rabbit antibodies [Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 January; 54(1): 225–230] Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to the macrocyclic trichothecene roridin A. [Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 September; 54(9): 2328–2330] PubChem [Roridin A Daten] |
|
|
Verrucarin A C27H34O9 - CAS 3148-09-2 Vorkommen: Myrothecium roridum Literatur: Über die Struktur von Verrucarin A. Verrucarine und Roridine [Helvetica Chimica Acta Volume 48, Issue 1 , Pages 157 - 176; doi 10.1002/hlca.19650480117 - Registreirung erforderlich] Crystal Structure of Verrucarin A [Analytical Sciences Vol. 15 (1999) , No. 4 p. 403 - Volltext] PubChem [11934 - Verrucarin A Daten] |
|
|
Verrucarin B C27H32O9 - CAS 2290-11-1 Vorkommen: Myrothecium verrucaria; M. roridum Literatur: PubChem [6441510 - Verrucarin B Daten] |
|
|
Verrucarin J C27H32O9 - CAS 2290-11-1 Vorkommen: Myrothecium verrucaria Literatur: PubChem [6441510 - Verrucarin B Daten] |
Trichothecene wirken cytotoxisch durch die Hemmung der ribosomalen Proteinsynthese, indem sie sich an eine 60S-Einheit eukaryontischer Zellen binden. Der reaktionsfähige Teil der Trochothecene ist die Epoxid-Gruppe (deren Hydrolyse führt durch Deaktivierung).
Quellen und Literaturhinweise
[1] - G. G. Freeman, R. I. Morrison:
Metabolic products of Trichothecium roseum Link.
Biochemistry Journal, 45, 191-199, (1949), DOI 10.1042/bj0450191.
Kategorie: Stoffgruppen
Aktualisiert am 19. Juli 2023.
Permalink: https://www.internetchemie.info/chemie-lexikon/stoffgruppen/t/trichothecene.php
© 1996 - 2026 Internetchemie ChemLin